socketpair的用法
socketpair 的用法
函数原型: int socketpair(int domain, int type, int protocol, int filedes[2]);
/*************************************************/
参数说明:
domain: 套接字存在的通信域
AF_UNIX
AF_INET
type: 套接字类型
SOCK_STREAM
SOCK_DGRAM
SOCK_SEQPACKET
SOCK_RAW
protocol: 协议
大部分情况下都指定该参数为 0,
可以为 TCP、 UDP
filedes[2] : 一对套接字描述字
/*************************************************/
实例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void)
{
int sockets[2];
int child;
char buf[1024];
char data1[100];
char data2[100];
strcpy(data1, "What's you name ?\n");
strcpy(data2, "Huzy !\n");
/* 创建套接字偶对 */
if(socketpair(AF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0, sockets) < 0)
{
printf("Socketpair error!\n");
exit(-1);
}
/* 创建子进程 */
if( (child = fork()) == -1 )
{
printf("Fork error!\n");
exit(-1);
}
/* 父进程 */
if(child != 0)
{
// 关闭子进程的套接字
close(sockets[0]);
// 读取来自子进程的数据
if( read(sockets[1], buf, sizeof(buf)) < 0 )
printf("Reading sockets error !\n");
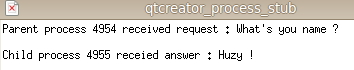
printf("Parent process %d received request : %s\n", getpid(), buf);
// 向子进程写数据
if(write(sockets[1], data2, sizeof(data2)) < 0)
printf("Writing socket error !\n");
// 关闭父进程套接字
close(sockets[1]);
}
/* 子进程 */
else
{
// 关闭父进程的套接字
close(sockets[1]);
// 向父进程写入数据
if( write(sockets[0], data1, sizeof(data1)) < 0 )
printf("Writing socket error !\n");
// 从父进程读取数据
if( read(sockets[0], buf, sizeof(buf)) < 0)
printf("Reading socket error !\n");
printf("Child process %d receied answer : %s\n", getpid(), buf);
// 关闭子进程套接字
close(sockets[0]);
}
}
运行截图:
顶(0)
踩(0)
- 最新评论
